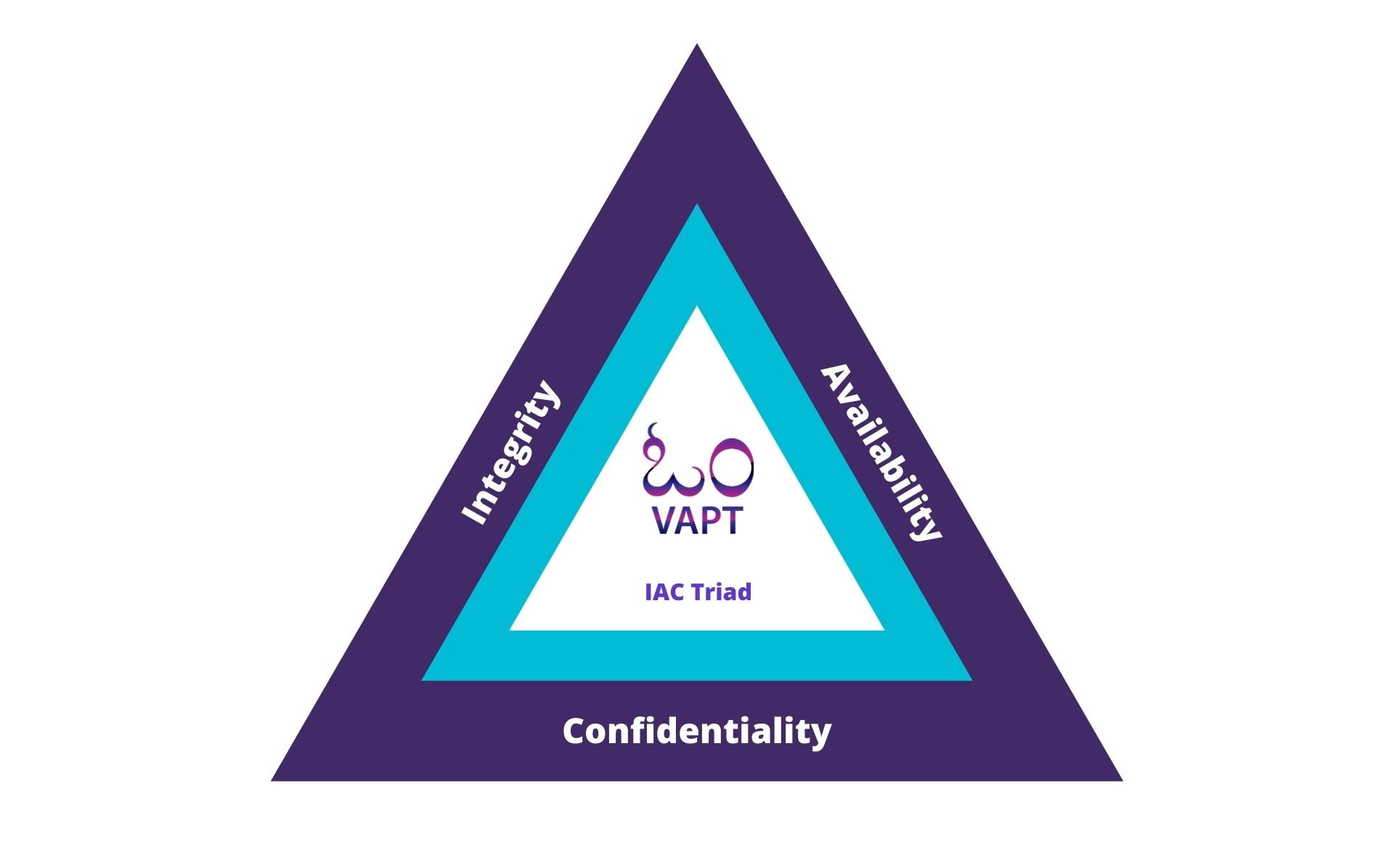
Confidentiality ensures that the necessary level of secrecy is enforced at each terminal of data processing and prevents unapproved or unauthorised exposure.
Integrity is sustained when the assurance of the accuracy and reliability of information and systems is provided and any unapproved change is blocked.
Availability protection ensures reliability and timely access to data and resources to approved individuals including insiders and outsiders.
Nonrepudiation Ensures that a sender cannot deny sending a message. Mechanisms include encryption, digital signatures, and notarization.
- Vulnerability Weakness or a lack of a countermeasure.
- Threat agent Entity that can exploit a vulnerability.
- Threat The danger of a threat agent exploiting a vulnerability.
- Risk The probability of a threat agent exploiting a vulnerability and the associated impact.
- Control Safeguard that is put in place to reduce risk, also called a countermeasure.
- Exposure Presence of a vulnerability, which exposes the organisation to a threat.
- Availability
- Redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID)
- Clustering
- Loadbalancing
- Redundant data and power lines
- Software and data backups
- Disk shadowing
- Co-location and off-site facilities
- Roll-back functions
- Fail-over configurations
- Integrity
- Hashing (data integrity)
- Configuration management (system integrity)
- Change control (process integrity)
- Access control (physical and technical)
- Software digital signing
- Transmission CRC functions
- Confidentiality
- Encryption for data at rest (whole disk, database encryption)
- Encryption for data in transit (IPSec, SSL, PPTP, SSH)
- Access control (physical and technical)
- Non-Repudiation
- Mutual Non-Compete Non-Disclosure Agreements.
- Digitally Signed Agreements.
A threat is any potential danger that is associated with the exploitation of a vulnerability.
A vulnerability is a lack of a countermeasure or a weakness in a countermeasure that is in place.
Exposure is an occurrence of being exposed to losses. A vulnerability exposes an organisation.
A risk is the likelihood of a threat agent exploiting a vulnerability and the corresponding business impact.
Key Important Aspects of Information Security.
- Elements of Information Security.
- Information Security Policies.
- Offensive Security (Branch of InfoSec).
- Information Security Frameworks.
- Information Security Governance.
- Information Risk Management.
benefits of infosec
profit centre
- Information Security is not a Cost Center. However, if you choose the right team then it is always a Profit Center.
- Preventing Costly Data Breaches and ensuring Business Continuity is the major aspect of Information Security.
- Having an Unbiased views about the Information Technology (IT) and IT Security are major goals.
- Building a Cyber Security Maturity Model and providing Security Awareness throughout the organisation enabling all people plays a vital role in making the human firewall.
- There is no patch to human stupidity. However, with proper Security Training and Security Policies the information risk will be mitigated.